Gestational Diabetes
Understanding Gestational Diabetes: A Quick Guide for Moms-to-Be
Disclaimer: Please note that all tips shared in this article are based on personal experience and are not intended as medical advice; always consult with your healthcare provider to ensure the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that can develop during pregnancy. It happens when your body can’t make enough insulin to keep your blood sugar levels in check. This can lead to higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, which isn’t great for you or your baby. The good news? With the right care, you can manage it and keep both you and your baby healthy.
What Causes Gestational Diabetes?
There’s no single cause, but a few factors can increase your risk, like being overweight, having a family history of diabetes, or being over 25. Pregnancy hormones can also make it harder for your body to use insulin, which is why gestational diabetes develops.
Symptoms to Watch For
Gestational diabetes doesn’t always come with clear symptoms. Some women might feel extra thirsty, need to pee more often, or feel more tired than usual. However, these are also common pregnancy symptoms, so regular screening is important.
Possible Consequences
If left unmanaged, gestational diabetes can lead to complications like a larger baby, which can make delivery more difficult, or a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later on. But with proper care, most women go on to have healthy pregnancies and babies.
Managing Gestational Diabetes: Focus on Food
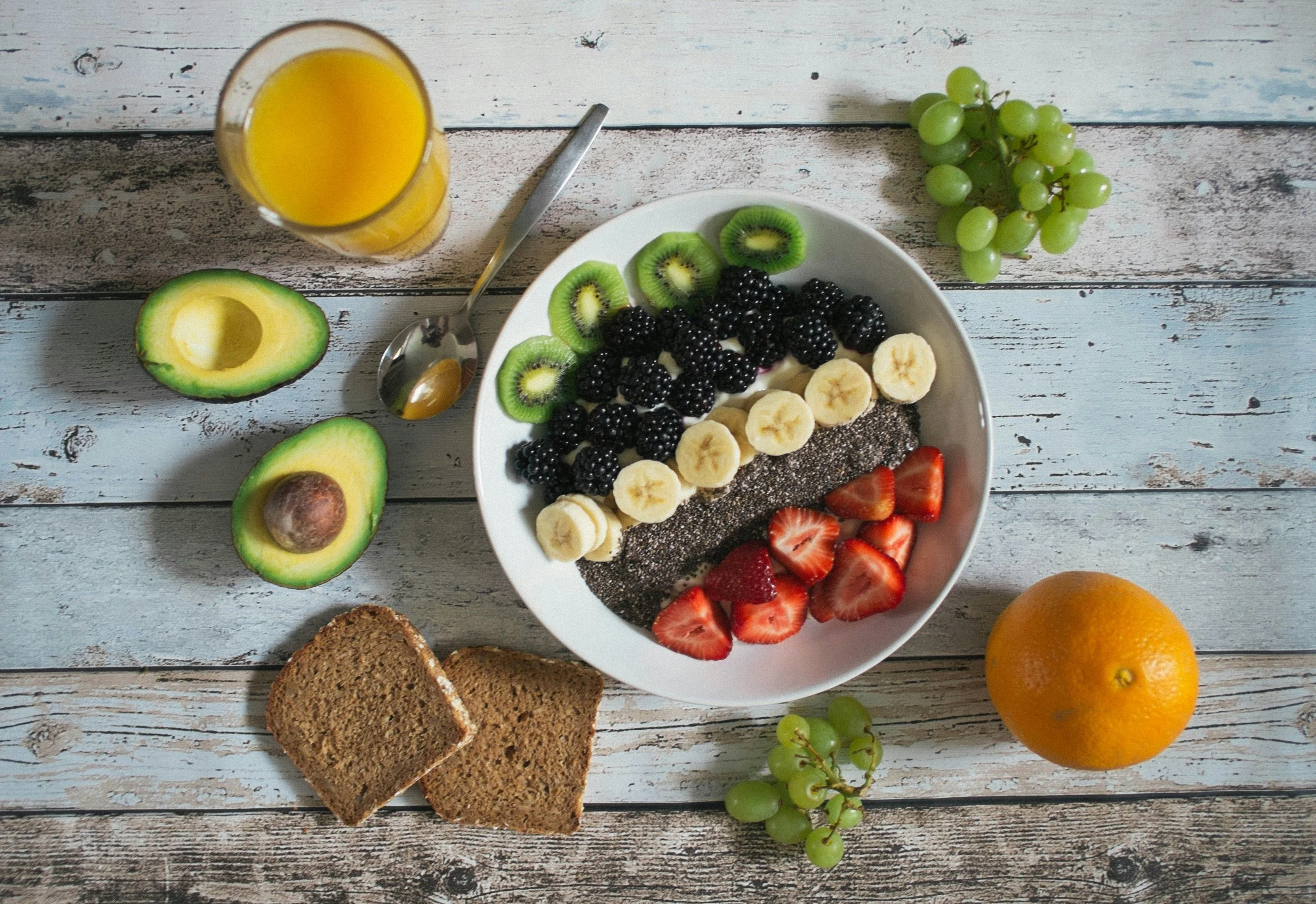
When it comes to controlling gestational diabetes, your diet is one of the most important tools you have. Making smart food choices can help keep your blood sugar levels stable, which is crucial for both your health and your baby’s. Here’s a more detailed look at how to manage your diet effectively:
1. Eat Regular, Balanced Meals and Snacks
Instead of sticking to three large meals, aim for three smaller meals with healthy snacks in between. This keeps your blood sugar steady throughout the day. For example:
Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with a slice of whole-grain toast.
Morning Snack: Greek yogurt with a handful of almonds.
Lunch: Grilled chicken with a side of quinoa and steamed veggies.
Afternoon Snack: A small apple with peanut butter.
Dinner: Baked salmon, brown rice, and a green salad.
2. Choose Complex Carbs Over Simple Carbs
Complex carbohydrates, like whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, take longer to digest, which helps prevent blood sugar spikes. Avoid simple carbs such as white bread, sugary drinks, and sweets, which can quickly raise your blood sugar. For example:
Swap white rice for brown rice or quinoa.
Choose whole-grain or sprouted grain bread over white bread.
Opt for snacks like carrot sticks, hummus, or berries instead of cookies or chips.
3. Pair Carbs with Protein
When you eat carbohydrates, pair them with protein to slow down the absorption of sugar into your bloodstream. This helps keep your blood sugar levels more stable. Good combinations include:
An apple with a handful of almonds.
Whole-grain crackers with cheese.
Oatmeal topped with chia seeds and a spoonful of peanut butter.
4. Watch Portion Sizes
Even healthy foods can raise your blood sugar if eaten in large amounts. Pay attention to portion sizes, especially when it comes to carbs. Here are some tips:
Use a measuring cup to portion out foods like rice or pasta.
Fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables, a quarter with protein, and a quarter with whole grains or starches.
Limit fruit servings to a small piece or ½ cup at a time, as fruit contains natural sugars.
5. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential for managing blood sugar levels. Water helps your body process glucose more efficiently and keeps you feeling full, which can prevent overeating.
6. Include Fiber-Rich Foods
Fiber slows the absorption of sugar and helps keep you full. Foods high in fiber include vegetables, fruits (in moderation), beans, lentils, and whole grains. Adding a salad with leafy greens to your meals or snacking on raw veggies can help increase your fiber intake.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively manage gestational diabetes and maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Remember, it’s all about balance and consistency. Working closely with your healthcare provider or a dietitian can also help tailor these tips to your specific needs, ensuring you and your baby stay healthy throughout your pregnancy.